What is a Knowledge Graph?
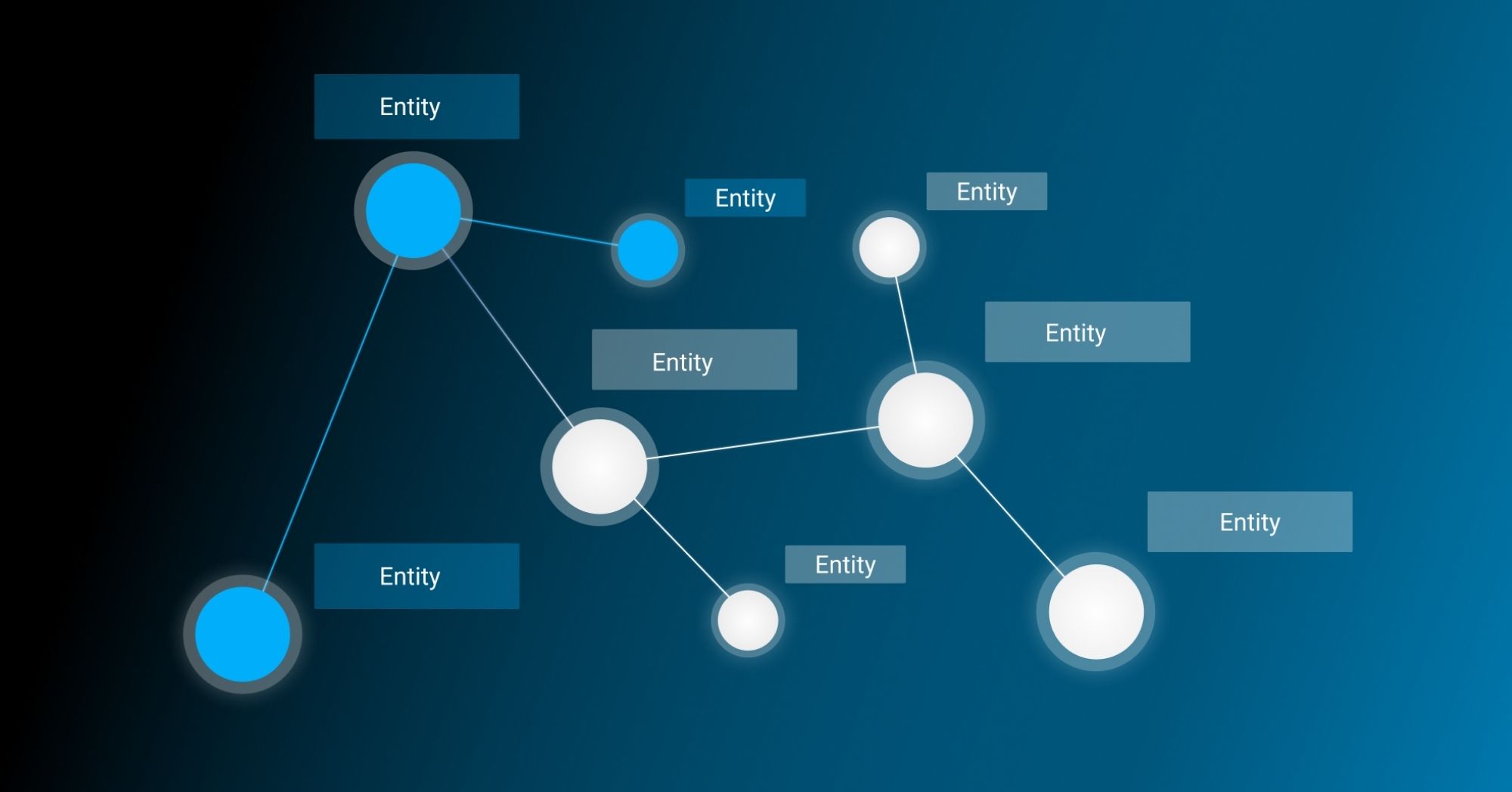
A knowledge graph is a semantic network that visualises entities and the relationships between them. The information represented by the Knowledge Graph is stored in a graph database.
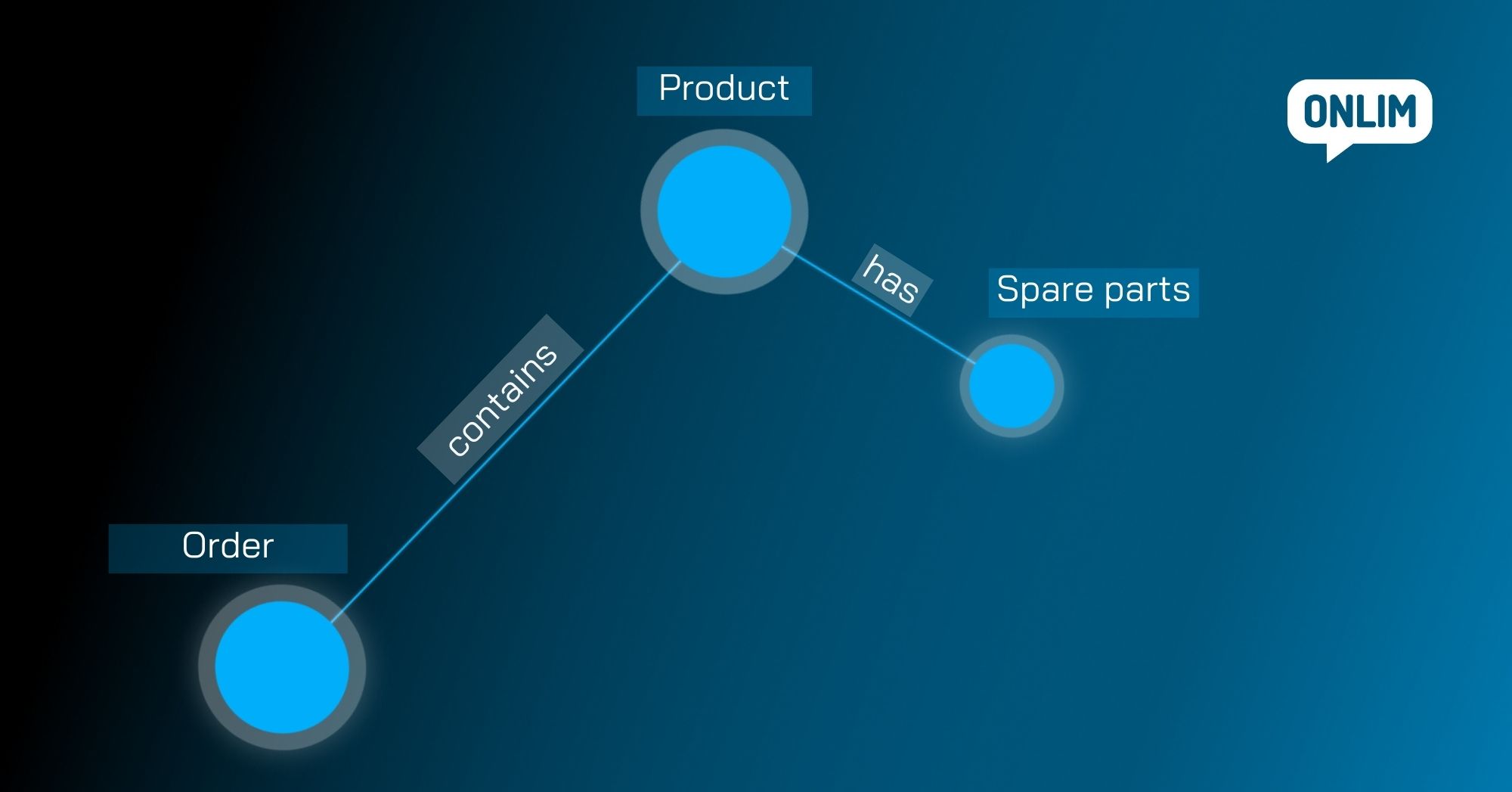
An entity is a real object such as an event or a person. In a Knowledge Graph, these real objects are represented as nodes. Each node/entity is related to other nodes/entities. The relationships are represented by edges – connections between the nodes. Edges can, for example, have the meaning “is part of”, “works at” or “has properties”.
For example, one node could be a product and another node could be an order. The edge between the product and the order represents the relationship between the two entities and indicates that a particular product belongs to a particular order.
By connecting the nodes via the edges, i.e. the relationships between the individual objects, a knowledge network is created. As you can see: a Knowledge Graph makes it possible to organise and link information and knowledge in a structured way.
What is the ontology of a Knowledge Graph?
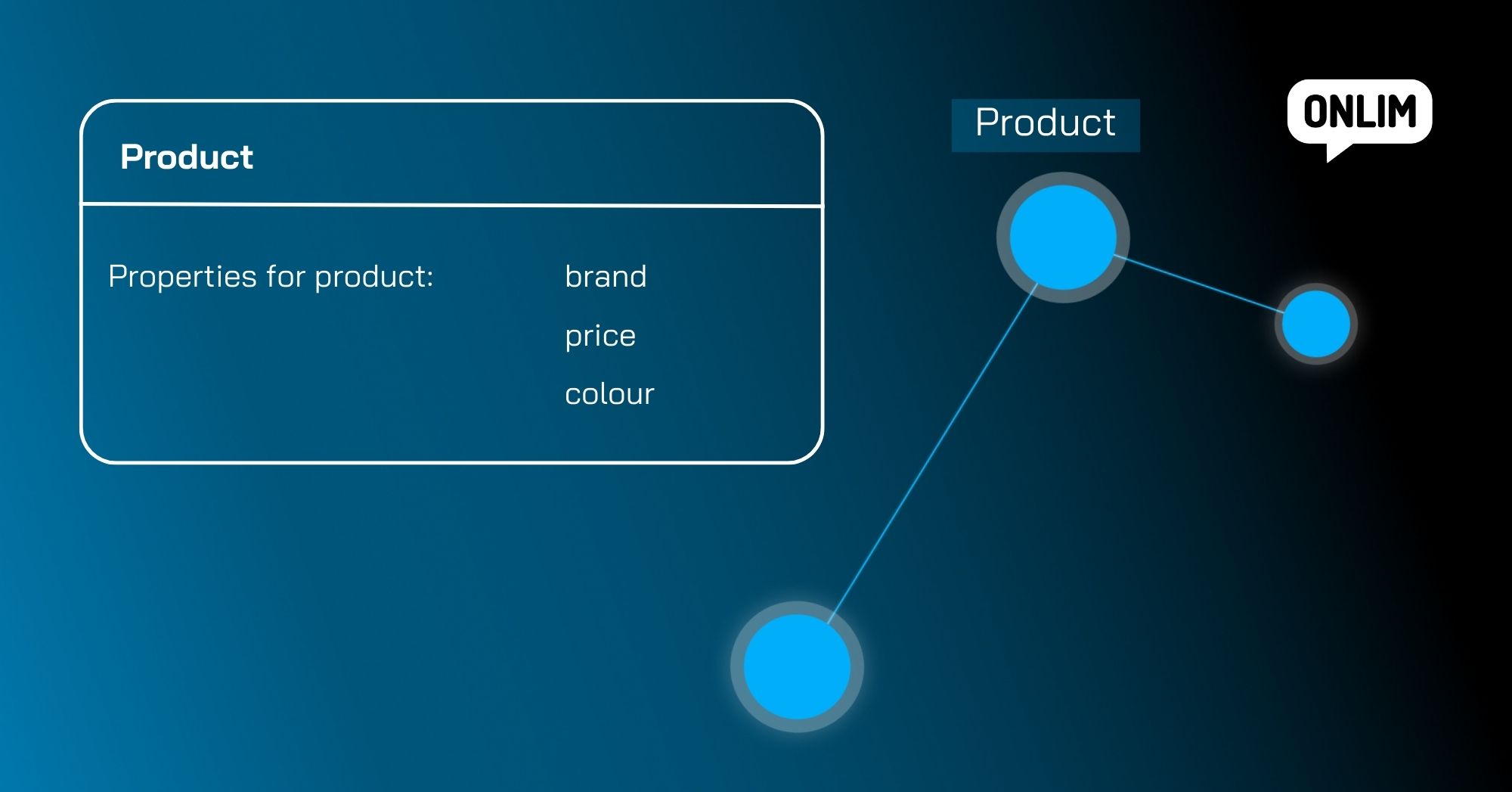
An ontology is a formal representation and description of knowledge about a particular domain. It is a type of knowledge model that formalises the concepts, categories, properties and relationships within a domain and presents them in a structured form.
An ontology enables knowledge to be structured in the Knowledge Graph. It is used to create a formal representation of the entities in the Knowledge Graph. They are based on a taxonomy.
How does a Knowledge Graph work?
Technically, a knowledge graph is based on a graph database. The graph database stores the nodes and edges of the knowledge graph as well as the associated metadata. The nodes and edges are represented as RDF triples consisting of a subject, a predicate and an object. The subject and the object represent the nodes, while the predicate represents the edge.
An important aspect of creating a Knowledge Graph is the semantic enrichment of the data. This means that the data is enriched with additional information that more precisely describes the meaning and relationships between the nodes and edges. This can be done by using ontologies.
To create and update the Knowledge Graph, various technologies are used, for example:
NLP (Natural Language Processing) to extract information from texts
Machine Learning for automatic identification of entities and relationships
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to integrate data from different sources
Data is added to the graph database when it is created or updated and can be retrieved and analysed using a query language such as SPARQL. As new data is added, individual objects are identified and the relationships between different objects are understood. This knowledge is then compared and integrated with other relevant and similar data sets.
When a knowledge graph is complete, question-answering and search systems can retrieve and reuse comprehensive answers to given queries.
More Knowledge For Chatbots And Voice Assistants
What are the advantages of a Knowledge Graph?
In general, a Knowledge Graph provides an effective way to organise and present information to facilitate the understanding of complex relationships and to enable effective data analysis. Specifically, the strength of a Knowledge Graph lies in the following aspects:
Simplified data integration: a Knowledge Graph helps to simplify the integration of different data sources by creating a common structure that can be applied to all data sources.
Better search results: By structuring the information in the Knowledge Graph, search queries can be answered more precisely because the relationships between different data objects are taken into account.
Effective knowledge representation: A Knowledge Graph can represent knowledge in an effective way by visualising relationships between different entities and concepts.
Contextualised information: Information can be presented in context, making it easier to understand complex relationships.
Automated analysis: A Knowledge Graph can serve as a basis for automated analysis and decision making, as it provides a structured representation of information that can be easily processed.
Improved data quality: The quality of data can be improved with the help of a Knowledge Graph, as it checks relationships between different entities and concepts and thus detects possible errors.
Flexibility: A Knowledge Graph is flexible and can be easily adapted to new requirements by adding new entities and concepts.
Conclusion
Knowledge graphs are a powerful technology that allows knowledge and information to be organised and linked in a structured way. They have a wide range of applications and can help companies use their knowledge more effectively and make better decisions.
With the further development of semantic technologies and the increase of data sources, Knowledge Graphs are becoming more and more important for the management and evaluation of knowledge.
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
March 18th, 2024|
What are chatbots and how do they work?
November 23rd, 2023|
The AI Act and its impact on the use of chatbots
October 27th, 2023|



